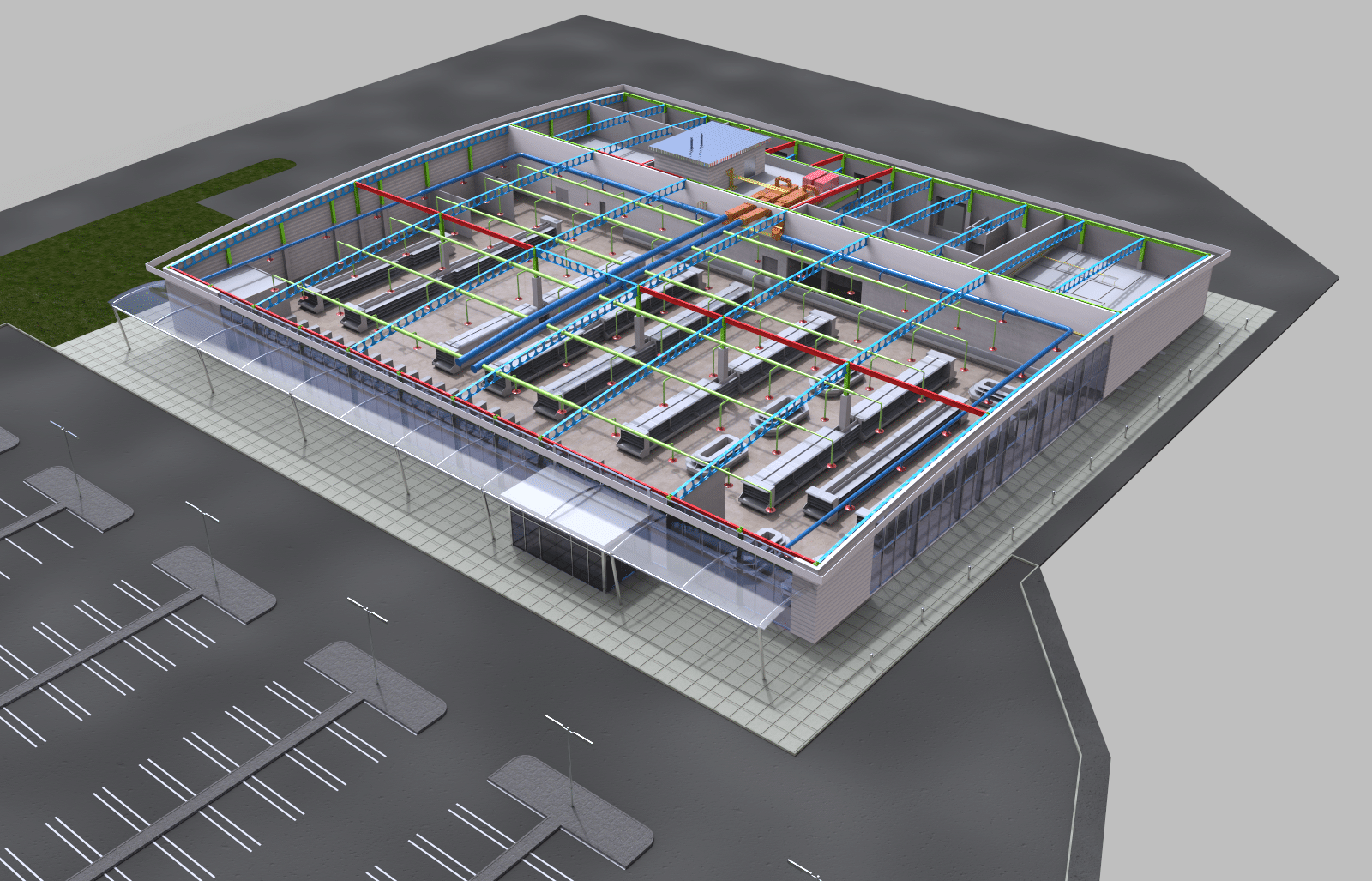
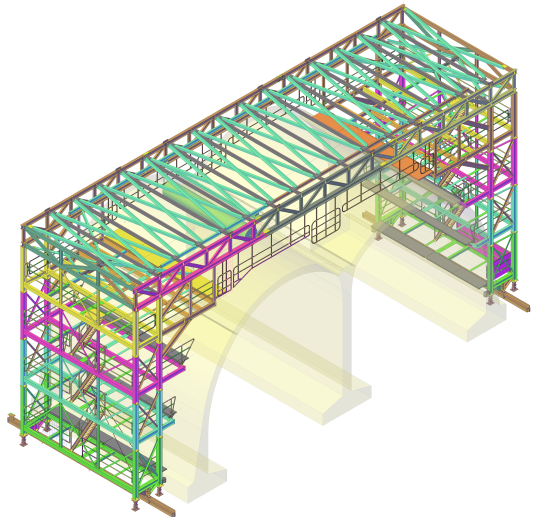
The interplay between business information modelling (BIM) and Health & Safety is crucial in safety-sensitive work environments. Not only could BIM build more auditable compliance and provide harvestable data for the HSE, it could also reduce accidents and potentially save lives.
This is particularly true on construction sites, but also applicable to any major repair or maintenance project with a degree of risk to the workers.
Previously, the value of BIM was perhaps perceived entirely in designing structures or sites, or working out cost effective ways to complete complex building and repair projects. However, there is an increasing awareness that BIM can improve occupational safety standards and build far greater hazard perception.
This is because BIM brings together a tool box of graphics and data, materials which can be used to communicate and rehearse. This includes, for example, integrating and generating digital representations, animations and renderings, reports and analysis, schedule simulation and lifecycles.
Having such a large shareable resource – including 4D digital representations of the physical and functional characteristics of a site or structure – provides far greater opportunities to form reliable decisions. This, in turn, could make a substantial contribution to reducing site risks.
Construction, repair and maintenance teams can be briefed off site in a meaningful way, as preparation for far more efficient and informed work practices.
Communication
Many of the industries associated with sites with safety issues are ones with entrenched methods of communication – tried and trusted ways to collaborate and inform. They are also potentially the teams who rely most of their individual experiences and perceptions to make judgements.
One of the biggest advantages of using business information modelling to disseminate information is that it can challenge assumptions, offer discuss points and validate solutions.
Having visual representations of structures and sites can also lead to new safety checks and measures. BIM gives the entire team the same reference points. It can help them visualise the characteristics and life cycle of a construction project or complex repair task in a way that creates a more unified and streamlined perception.
Predictive data
One of the most visual ways to illustrated Health & Safety risks is to actually show what happens when things go wrong. Clearly, this is far easier with animation and rendering than in real life.
BIM can be used to forecast what would happen without due care and attention and adherence to procedures, or to map out and discuss how unexpected or seasonal variations can impact on risk factors. For example, Hurricane Irma recently damaged tower cranes in the USA considered to be weather-proof.
Crews could be far more mindful having seen the lifecycle of a project and the different ways in which mistakes have long term repercussions. Using predictive data to create 4D imagery can also give teams the chance to rehearse reactions to situations.
Greater project control
However, some of the advantages of using BIM to manage construction sites and major repair projects are more mundane than that.
It can provide insights on all aspects of the project – from the initial plan and the materials being used to the potential snagging points. This level of transparency and control reduces waste, streamlines scheduling and, therefore, manages the project and the workforce in a more regulated fashion.
Employee engagement
BIM usually includes a planned schedule of work. This data can be used to create 4D models showing the construction or repair process over time.
This is not just a significant tool in illustrating how contractual obligations have been met. It also offers each team member a way of visualising their own contribution. The increased ownership and engagement this brings is likely to make them far more switched on to quality standards and the necessity for safety regulations.
Using realistic simulation, business information modelling, therefore, offers safety-sensitive workplaces multiple benefits. This includes intuitive control of construction and major repair projects, keeping them on schedule and within budget. It can also play a significant role in underpinning quality, compliance with Health & Safety regulations and risk reduction.
Sources:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4372221/
http://www.bimplus.co.uk/management/where-does-bim-stand-health-and-safety/